The Link Between PArkinsons Disease and Cannabis
Medical Marijuana is used recreationally by many people to self-medicate symptoms of neurological disorders such as Parkinsons Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, ALS, and Schizophrenia. In fact, about 44% of people with Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and MS is currently using Cannabis. Although there is not sufficient proof that Cannabis can cure or relieve symptoms associated with Parkinsons Disease, some studies and current Cannabis users report lower levels of disability.
How does Cannabis work for Parkinsons Disease?
Our bodies make natural Cannabinoids called Endocannabinoids that help regulate functions like sleep, appetite, mood, and other processes by binding to receptors throughout the body and brain. The the main two receptors are called CB1 and CB2 receptors.
The Cannabis plant contains 144 cannabinoids called Phytocannabinoids, as well as other therapeutic components like terpenes, flavonoids, and amino acids. When we ingest or inhale Cannabis, the cannabinoids within the plant are able to act just like our Endocannabinoids and attach to our receptors to initiate a regulations response.
The Phytocannabinod THC attaches to the CB1 receptors and Cannabinoil (CBD) attaches to CB2 receptors. There are other Phytocannabinoids that attach to other receptors in our bodies, but for Parkinsons Disease we will concentrate on CB1 Receptors. Each receptor in our body has a different job, or controls a certain function. We can find all receptors throughout our whole body. The majority receptors found in the brain are CB1, therefore when considering regulation of brain functions related in Parkinsons Disease, THC is the main Cannabis Cannabinoid beneficial to managing symptoms of PD.
CB1 receptors are found in particularly high numbers in the basal ganglia, a circuit of brain cells that controls movement and is affected in Parkinson’s.
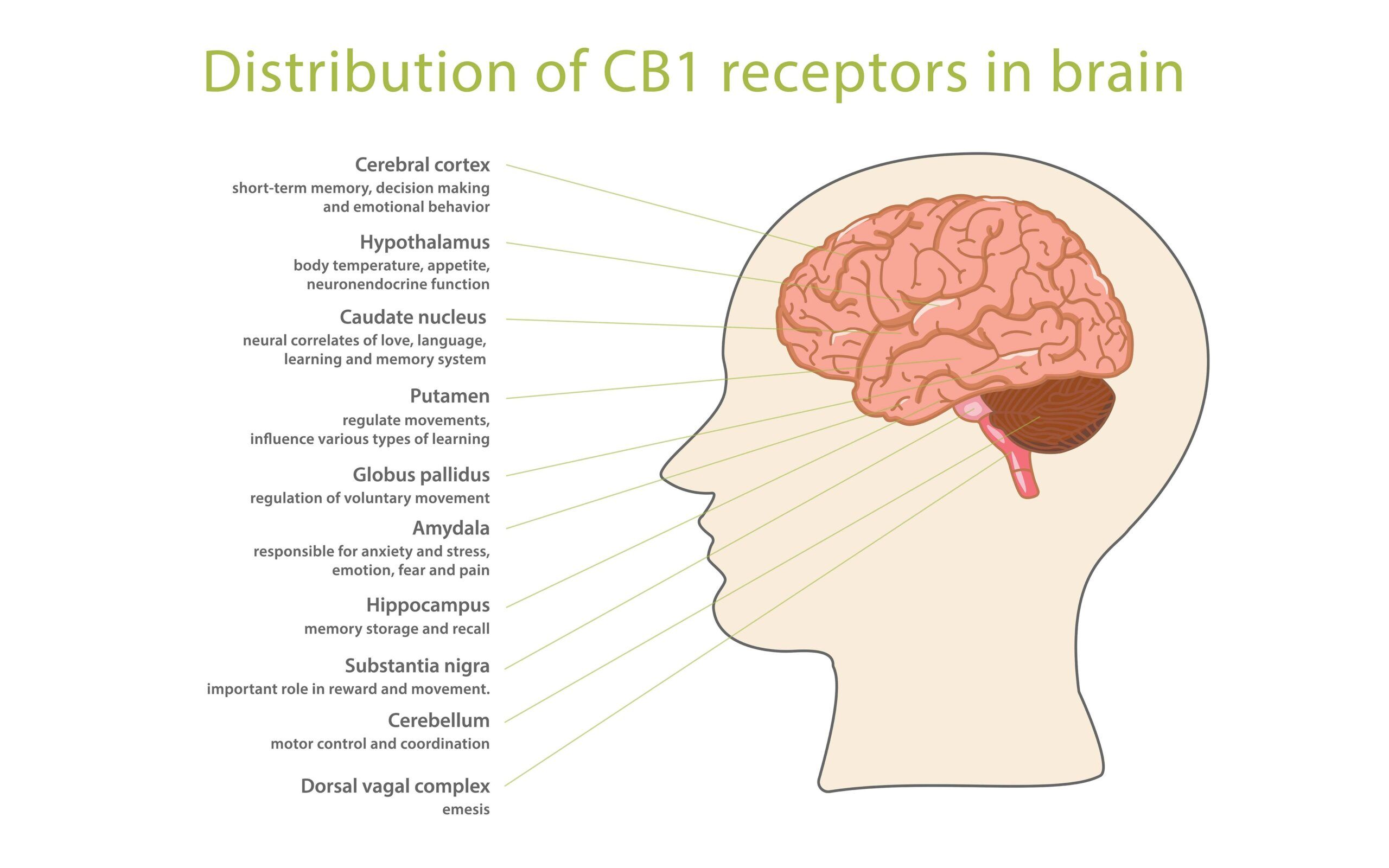
The Basal Ganglia are a group of structures found deep within the Cerebral Hemispheres. Out of the list provided in this image, the following structures are within the Basal Ganglia, and directly involved with Parkinson’s Disease:
Related Products
-
Caudate Nucleus
-
Putamen
-
Globus Pallidus
-
Substantia Nigra
-
Cerebellum
Some of Parkinsons Disease most noticeable and most debilitating characteristics are Tremors, Stiffness, Slowness of Movement, and Impaired Balance and Coordination. This happens when our nerve cells, or neurons, in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and/or die. When working properly, these neurons produce an important chemical for the brain called Dopamine. When they are impaired or die they are unable to produce as much Dopamine, which causes the movement problems of PD. People with Parkinsons Disease also loose the nerve endings that produce Norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system that controls many automatic functions of the body. This involves very important functions like heart rate and blood pressure.
There is a significant presence of cannabinoid receptors in the basal ganglia, Globus pallidus and Substantia Nigra, the major brain areas involved in the control of movements. Because the Cannabinoids in the Cannabis Plant bind to these receptors and regulate nerve pathways, researchers have looked at whether they could modify the course of PD with Cannabis. Essentially, it appears that when THC binds to the receptors in the Basal Ganglia, a regulatory response is created, repairing the neurons and nerve endings that are damaged. This enables them to replenish the loss of Dompamine and Norepinephrine detected in Parkinsons Disease.
Almost immediately after taking THC and CBD, most people with Parkinson’s Disease feel some sort of relief. Many of these people report significant decrease in tremors and Dyskinesia (caused by long term use of the only medication prescribed for Parkinson’s, Levodopa). Others benefit more from the ability to sleep at night. Either way, the consumption of Cannabinoids have evidently provided relief and a better quality of life for people suffering from Parkinsons Disease. Doctors are concerned that people with Parkinsons may develop a dependency on Cannabis if it is used regularly but Parkinsons patients seem to feel the trade off is much more beneficial than harmful.
Watch these following videos to witness how instantly Cannabis relieves motor control symptoms for these Parkinsons patients, it is simply AMAZING!
Which Cannabis product should I try for Parkinsons Disease?
For Parkinsons, you can smoke Cannabis flower (Marijuana), or you can ingest THC in an oil form. Using a concentrate like oil makes it easier to monitor the dose that is right for you. The goal is to only take as much as you need to find relief from symptoms. This amount will be a little bit different for everyone because our bodies respond with Cannabinoids differently so it is smart to start with micro doses and work your way up.
When taking a THC product, like Phoenix Tears, it is helpful to take a CBD product, like CBD Full Spectrum Oil, with it. CBD will help level out any psychoactive effects from the THC and provide a more balanced feeling while using a Cannabis product. Furthermore, when each cannabinoid like THC and CBD (as well as other cannabinoids present in Cannabis products) are taken together the medicinal benefits of each are enhanced and prolonged.
The TLCBD Family encourages you to reach out if you are unsure which products to use and how to use them. We have experience with many customers who have turned to Cannabis to relieve their symptoms. We would gladly guide you in the right direction! Please email us at contact@mytlcbd.ca